2024 年强劲的 Java 语言特性
Ana-Maria Mihalceanu 于 2024 年 1 月 16 日无论您是初学者还是资深 Java 开发人员,您都努力通过代码实现雄心勃勃的目标,同时享受渐进式进步。除了许多性能、稳定性和安全性更新之外,Java 21 还提供了旨在提高 Java 开发效率的新功能和增强功能。学习这些语言特性的最佳方法是在 Java 项目中使用它们。
设置
12 月的假期已经过去,但还有许多其他机会可以提供礼物。因此,让我们构建一个 Java 应用程序,您可以在其中为某人订购一份包装好的礼物。项目 wrapup 是一个简单的 http 处理程序实现,它通过 HTTP POST 方法从发件人到收件人以 JSON 格式返回礼物。
在开始行动之前,您应该知道您需要一个 IDE,至少需要在本地机器上安装 JDK 21 和 Maven 来重现示例。我使用 Oracle Java Platform Extension for Visual Studio Code 通过 View > Command Palette > Java: New Project > Java with Maven 生成了我的项目,将项目命名为 wrapup 并选择了包名 org.ammbra.advent。
因此,让我们看看如何使用 Java 21 语言结构将礼物打包成 JSON。
走向 Java 的简化起点
IDE 生成的项目包含一个启动类 Wrappup.java,位于包 org.ammbra.advent 中。
package org.ammbra.advent;
public class Wrapup {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello World!");
}
}
虽然 main 方法声明了参数,但这些参数后来并没有在其范围内被处理。在 JDK 21 中,JEP 445 引入了无名类和实例 main 方法作为预览功能,以减少编写简单程序时的冗长性。因此,您可以将之前的代码重构为
package org.ammbra.advent;
class Wrapup {
void main() { System.out.println("Hello, World!");}
}
要运行前面的代码片段,请转到终端窗口并键入以下命令
java --enable-preview --source 21 src/main/java/org/ammbra/advent/Wrapup.java
目前,让我们将 Wrapup 类演变为仅处理 HTTP POST 请求并生成 JSON 输出,方法是实现 com.sun.net.httpserver.HttpHandler。
class Wrapup implements HttpHandler {
void main() throws IOException {
var server = HttpServer.create(
new InetSocketAddress("", 8081), 0);
var address = server.getAddress();
server.createContext("/", new Wrapup());
server.setExecutor(Executors.newVirtualThreadPerTaskExecutor());
server.start();
System.out.printf("http://%s:%d%n",
address.getHostString(), address.getPort());
}
@Override
public void handle(HttpExchange exchange)
throws IOException {
int statusCode = 200;
String requestMethod = exchange.getRequestMethod();
if (!"POST".equalsIgnoreCase(requestMethod)) {
statusCode = 400;
}
// Get the request body input stream
InputStream reqBody = exchange.getRequestBody();
// Read JSON from the input stream
JSONObject req = RequestConverter.asJSONObject(reqBody);
String sender = req.optString("sender");
String receiver = req.optString("receiver");
String message = req.optString("celebration");
String json = "{'receiver':'" + receiver
+ "', 'sender':'" + sender
+ "','message':'" + message + "'}";
exchange.sendResponseHeaders(statusCode, 0);
try (var stream = exchange.getResponseBody()) {
stream.write(json.getBytes());
}
}
}
该项目依赖于 Maven 进行依赖项管理,为了处理 JSON,您应该修改 pom.xml 以包含 json 依赖项
<dependency>
<groupId>org.json</groupId>
<artifactId>json</artifactId>
<version>${json.version}</version>
</dependency>
要启动程序,您不需要使用 mvn 功能,您可以直接使用 java/javac,方法是转到终端窗口并运行
#export path to .m2 json library
export $JSON_PATH=/<YOU>/.m2/repository/org/json/json/20231013
#launch the app
java -classpath $JSON_PATH/json-20231013.jar --enable-preview --source 21 \
src/main/java/org/ammbra/advent/Wrapup.java
如果您的操作系统是 Windows,请转到 命令提示符 窗口并运行
set JSON_PATH=C:\.m2\repository\org\json\json\20231013
java -classpath $JSON_PATH/json-20231013.jar --enable-preview --source 21
src/main/java/org/ammbra/advent/Wrapup.java
让我们尝试一个简单的 curl 请求来检查输出
curl -X POST http://127.0.0.1:8081 -H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{"receiver":"Duke","sender":"Ana","celebration":"Happy New Year!"}'
您应该收到以下响应
{'receiver':'Duke', 'sender':'Ana','message':'Happy New Year!'}
向某人打招呼是一个不错的举动,但当发件人希望发送更实质性的礼物时,该应用程序还应该提供更复杂的响应。为了解决这个问题,让我们对应用程序域进行建模。
使用记录和密封类型进行数据建模
在特殊场合赠送礼物可以从明信片到更实质性的礼物不等。
对于 wrapup 项目,让我们考虑以下要求
- 发件人可以做一个友好的举动,并提供一份礼物。
- 礼物可以是明信片,也可以在明信片的基础上添加以下内容之一:在线优惠券、购买体验或实物礼物。
- 明信片没有关联的成本,其他 3 种类型的礼物都有价格。
- 在线优惠券有过期日期。
- 礼物可以放在盒子里,盒子有额外的成本。
- 发件人可以根据庆祝活动赠送不同的明信片或惊喜,但绝不会将 2 张明信片作为礼物发送。
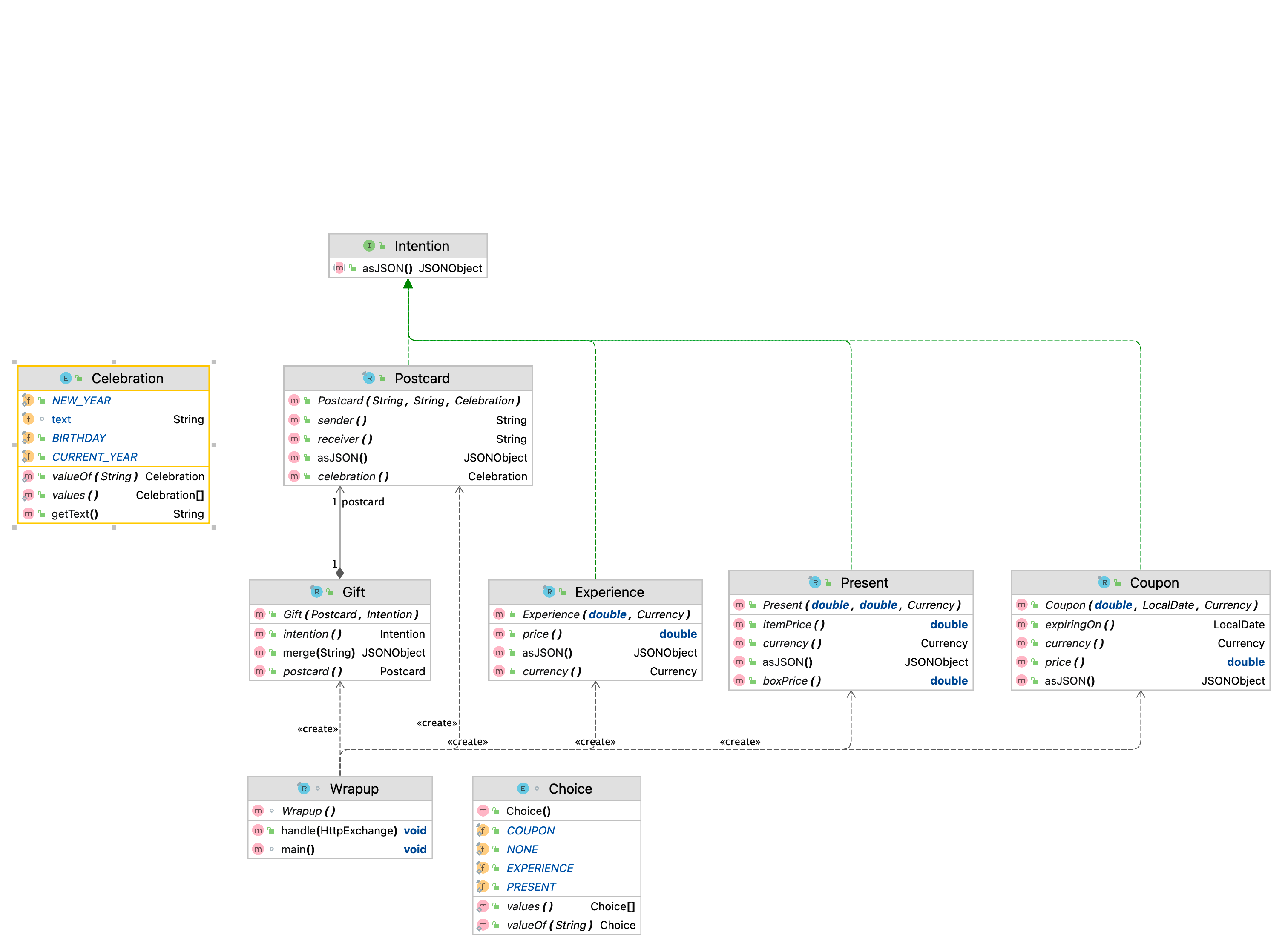 图 1 项目类图
图 1 项目类图
上面的图表显示了对先前描述的场景进行建模的一种可能方式。 Postcard、Coupon、Experience 和 Present 是记录,因为它们应该是不可变数据的载体,代表可能的惊喜选项。它们还通过密封接口 Intention 共享一个通用的 JSON 格式化过程。
package org.ammbra.advent.surprise;
import org.json.JSONObject;
public sealed interface Intention
permits Coupon, Experience, Present, Postcard {
JSONObject asJSON();
}
一个 Gift 是另一种记录类型,包含一个 Postcard 和一个 Intention。
package org.ammbra.advent.surprise;
import org.json.JSONObject;
public record Gift(Postcard postcard, Intention intention) {
public JSONObject merge(String option) {
JSONObject intentionJSON = intention.asJSON();
JSONObject postcardJSON = postcard.asJSON();
return postcardJSON.put(option, intentionJSON);
}
}
Celebration 是一个枚举,存储发送礼物的定义场合。根据 Choice 枚举的值,wrapup 将以 JSON 格式返回相应的礼物。接下来,让我们定义 Coupon、Experience、Postcard 和 Present 记录,并使用字符串模板格式化它们的数据。
具有表达力字符串模板的语法灵活性
密封接口 Intention 限制了继承,只允许特定的子类型,但它也是一个有用的语言结构,用于传达 Coupon、Experience、Postcard 和 Present 记录的目的。例如,Coupon 对象的特征是它的价格、过期日期和成本的货币。由于礼物表示应该遵循 JSON 格式,让我们利用字符串模板来实现这一点。
字符串模板作为 Java 21 中的预览功能 提供,并将 在 JDK 22 中获得第二次预览。字符串模板将文字文本与嵌入式表达式和模板处理器混合在一起,以生成专门的结果,例如 JSONObject。要返回一个 JSONObject,模板表达式需要
- 一个模板处理器 (
JSON) - 一个点字符 (
U+002E) 和 - 包含嵌入式表达式的模板 (
Coupon记录字段)。
Coupon、Experience、Postcard 和 Present 记录可以从字符串到 JSON 共享相同的模板处理器
package org.ammbra.advent.surprise;
import org.json.JSONObject;
public sealed interface Intention
permits Coupon, Experience, Present, Postcard {
StringTemplate.Processor<JSONObject, RuntimeException> JSON = StringTemplate.Processor.of(
(StringTemplate st) -> new JSONObject(st.interpolate())
);
JSONObject asJSON();
}
注意:为了简洁和清晰,本示例采取了一些捷径,并不一定实现了所有针对将投入生产的应用程序推荐的最佳实践(安全性、可扩展性、广泛的错误处理等)。例如,您应该考虑检查模板的值,并在值可疑时抛出已检查异常 (
JSONException)!
有了这个模板处理器,Coupon 记录就变成了
package org.ammbra.advent.surprise;
import org.json.JSONObject;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.util.Currency;
public record Coupon(double price, LocalDate expiringOn, Currency currency)
implements Intention {
public Coupon {
Objects.requireNonNull(currency, "currency is required");
if (price < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Price of an item cannot be negative");
}
}
@Override
public JSONObject asJSON() {
return JSON. """
{
"currency": "\{currency}",
"expiresOn" : "\{ expiringOn}",
"cost": "\{price}"
}
""" ;
}
}
Experience 和 Postcard 记录共享类似的模板格式化逻辑。由于 Present 的成本取决于礼品包装的成本,因此 asJSON 方法的实现如下
package org.ammbra.advent.surprise;
import org.json.JSONObject;
import java.util.Currency;
public record Present(double itemPrice, double boxPrice, Currency currency)
implements Intention {
public Present {
Objects.requireNonNull(currency, "currency is required");
if (itemPrice < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Price of an item cannot be negative");
} else if (boxPrice < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Price of the box cannot be negative");
}
}
@Override
public JSONObject asJSON() {
return JSON. """
{
"currency": "\{currency}",
"boxPrice": "\{boxPrice}",
"packaged" : "\{ boxPrice > 0.0}",
"cost": "\{(boxPrice > 0.0) ? itemPrice + boxPrice : itemPrice}"
}
""" ;
}
}
现在项目已经有了数据模型的每个元素,让我们研究如何对包含礼物的 JSON 的 HTTP 响应进行原型设计。
使用模式匹配在 switch 表达式中实现清晰的控制流
wrapup 应用程序的用户应该能够发出不同的请求,将个性化的礼物发送给某人
#send a postcard with a greeting for current year
curl -X POST http://127.0.0.1:8081 -H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{"receiver":"Duke","sender":"Ana","celebration":"CURRENT_YEAR", "type":"NONE"}'
#send a coupon and a postcard with a greeting for current year
curl -X POST http://127.0.0.1:8081 -H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{"receiver":"Duke","sender":"Ana","celebration":"CURRENT_YEAR", "option":"COUPON", "itemPrice": "24.2"}'
#send a birthday present and postcard
curl -X POST http://127.0.0.1:8081 -H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{"receiver":"Duke","sender":"Ana","celebration":"BIRTHDAY", "option ":"PRESENT", "itemPrice": "27.8", "boxPrice": "2.0"}'
#send a happy new year postcard and an experience
curl -X POST http://127.0.0.1:8081 -H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{"receiver":"Duke","sender":"Ana","celebration":"NEW_YEAR", "option ":"EXPERIENCE", "itemPrice": "47.5"}'
为了支持所有这些操作,自定义的 HTTPHandler 应该能够处理每个请求主体并返回相应的礼物作为 JSON。鉴于 POST 请求主体的复杂性,让我们将其表示为一个基于潜在数据的记录
package org.ammbra.advent.request;
import org.ammbra.advent.surprise.Celebration;
public record RequestData(String sender, String receiver,
Celebration celebration, Choice choice,
double itemPrice, double boxPrice) {
private RequestData(Builder builder) {
this(builder.sender, builder.receiver,
builder.celebration, builder.choice,
builder.itemPrice, builder.boxPrice);
}
public static class Builder {
private String sender;
private String receiver;
private Celebration celebration;
private Choice choice;
private double itemPrice;
private double boxPrice;
public Builder sender(String sender) {
this.sender = sender;
return this;
}
public Builder receiver(String receiver) {
this.receiver = receiver;
return this;
}
public Builder celebration(Celebration celebration) {
this.celebration = celebration;
return this;
}
public Builder choice(Choice choice) {
this.choice = choice;
return this;
}
public Builder itemPrice(double itemPrice) {
this.itemPrice = itemPrice;
return this;
}
public Builder boxPrice(double boxPrice) {
this.boxPrice = boxPrice;
return this;
}
public RequestData build() throws IllegalStateException {
return new RequestData(this);
}
}
}
RequestData 使用备用构造函数将 Builder 实例传递给记录构造函数。使用此记录定义,handle(HttpExchange exchange) 方法内的逻辑重构为
@Override
public void handle(HttpExchange exchange) throws IOException {
// ...
// Get the request body input stream
InputStream reqBody = exchange.getRequestBody();
// Read JSON from the input stream
JSONObject req = RequestConverter.asJSONObject(reqBody);
RequestData data = RequestConverter.fromJSON(req);
// ... }
接下来,让我们根据请求中存在的礼物选项评估惊喜内容,并确保使用详尽的 switch 表达式对每种情况进行相应处理
double price = data.itemPrice();
double boxPrice = data.boxPrice();
Choice choice = data.choice();
Intention intention = switch (choice) {
case NONE -> new Coupon(0.0, null, Currency.getInstance("USD"));
case COUPON -> {
LocalDate localDate = LocalDateTime.now().plusYears(1).toLocalDate();
yield new Coupon(data.itemPrice(), localDate, Currency.getInstance("USD"));
}
case EXPERIENCE -> new Experience(data.itemPrice(), Currency.getInstance("EUR"));
case PRESENT -> new Present(data.itemPrice(), data.boxPrice(), Currency.getInstance("RON"));
};
如果没有默认分支,添加新的 Choice 值会导致编译错误,这将使我们考虑如何处理这些新情况。
由于礼物意图现在已经明确,让我们通过使用 switch 的模式匹配来处理最终的 JSONObject 响应。
Postcard postcard = new Postcard(data.sender(), data.receiver(), data.celebration());
Gift gift = new Gift(postcard, intention);
JSONObject json = switch (gift) {
case Gift(Postcard p1, Postcard p2) -> {
String message = "You cannot send two postcards!";
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(message);
}
case Gift(Postcard p, Coupon c)
when (c.price() == 0.0) -> p.asJSON();
case Gift(Postcard p, Coupon c) -> {
String option = choice.name().toLowerCase();
yield gift.merge(option);
}
case Gift(Postcard p, Experience e) -> {
String option = choice.name().toLowerCase();
yield gift.merge(option);
}
case Gift(Postcard p, Present pr) -> {
String option = choice.name().toLowerCase();
yield gift.merge(option);
}
};
在这种情况下,switch 表达式使用 Gift 的嵌套记录模式来确定最终的 JSON。如初始要求中所述,发送者不能将两张明信片作为礼物发送,因此不支持该操作。另一种特殊情况是发送者只提供一张免费明信片,而最终的礼物没有相关成本。因此,switch 表达式首先在受保护的 case 标签中处理这种情况 -case Gift(Postcard p, Coupon c) when (c.price() == 0.0)– 因为不受保护的模式 case 标签 -case Gift(Postcard p, Coupon c)– 覆盖了具有相同模式的受保护模式 case 标签。
记录和记录模式非常适合简化数据处理,但 Wrapup 程序只需要一些组件进行进一步处理。
使用未命名模式和变量的简洁代码
当 switch 对多个情况执行相同的操作时,您可以使用未命名模式变量来提高其可读性。未命名模式和变量在 JDK 21 中成为预览功能,目标是在 JDK 22 中最终确定(参见 JEP 456)。
先前 switch 表达式中的某些情况需要 Postcard、Coupon、Experience 和 Present,但从未使用过这些记录中的其他值。在使用未命名模式变量重构 switch 后,它变为
Gift gift = new Gift(postcard, intention);
JSONObject json = switch (gift) {
case Gift(Postcard _, Postcard _) -> {
String message = "You cannot send two postcards!";
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(message);
}
case Gift(Postcard p, Coupon c)
when (c.price() == 0.0) -> p.asJSON();
case Gift(_, Coupon _), Gift(_, Experience _),
Gift(_, Present _) -> {
String option = choice.name().toLowerCase();
yield gift.merge(option);
}
};
现在 Wrapup 实现已达到最终状态,请构建项目并从终端窗口再次启动它
#compile the sources
javac --enable-preview --source 21 -g -classpath $JSON_PATH/json-20231013.jar \
-sourcepath src/main/java -d target/classes src/main/java/org/ammbra/advent/Wrapup.java
#launch the app
java --enable-preview --source 21 -classpath $JSON_PATH/json-20231013.jar:target/classes \
src/main/java/org/ammbra/advent/Wrapup.java
并通过 curl 发出 POST 请求
curl -X POST http://127.0.0.1:8081 -H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{"receiver":"Duke","sender":"Ana","celebration":"NEW_YEAR", "option ":"EXPERIENCE", "itemPrice": "47.5"}'
如果您想进一步尝试本文中使用的代码,请访问 wrapup 存储库。
最后的想法
JDK 21 的预览功能,如字符串模板、未命名模式、变量、未命名类和实例 main 方法,可以帮助您最大限度地减少重复和冗长的代码量,使您能够更清晰、更简洁地表达意图。使用记录和密封类型来建模您的域,并使用记录模式和 switch 的模式匹配来启用强大的数据导航和处理形式。随着新年的开始,我鼓励您尝试这些功能,以提高您的 Java 生产力。
本文的内容最初在 The JVM Programming Advent Calendar 中分享。
